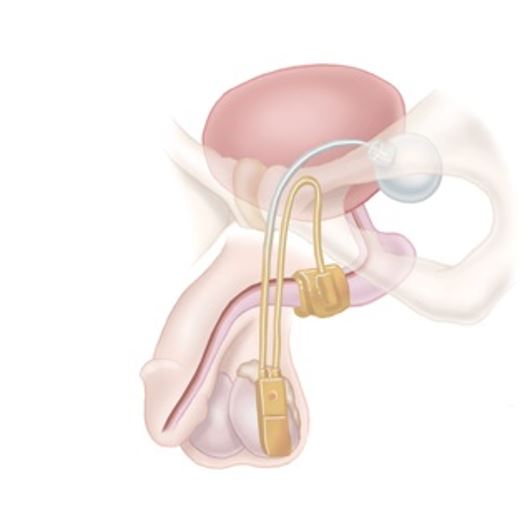
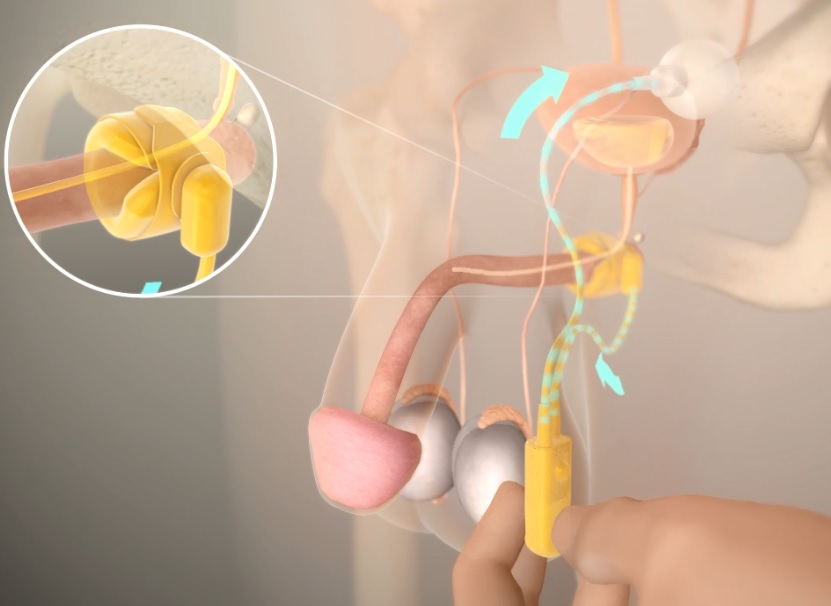
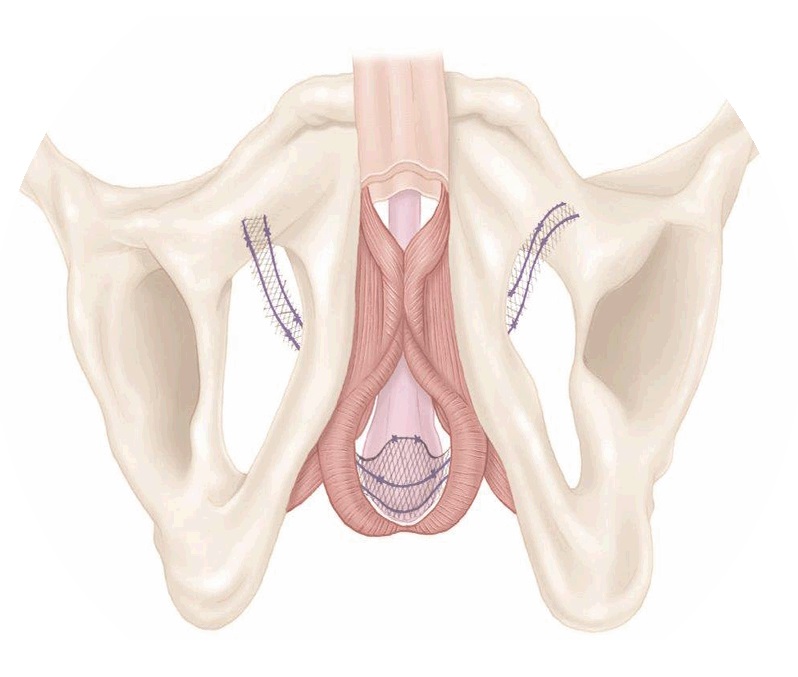
What you should know about long term solutions for incontinence
There are different solutions for incontinence beyond oral medications or pelvic floor exercises.1,5
Talking to a urologist about options like these could help you reclaim your quality of life.1–3
*Content of this video is for Information Purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Boston Scientific strongly recommends that you consult with your physician on all matters pertaining to your health or to address any questions.
Results from case studies are not necessarily predictive of results in other cases. Results in other cases may vary. All images are the property of Boston Scientific. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Disclaimer: Individual symptoms, situations, circumstances and results may vary. This information is not intended to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment or as a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult your doctor or qualified healthcare provider regarding your condition and appropriate medical treatment.
These Videos are meant for informational purposes only and may not be indicative of clinical outcome. The opinions, procedures and patient care policies expressed or depicted in the videos are those of the physician or practice nurse and do not necessarily reflect the opinions, policies or recommendations of Boston Scientific Corporation or any of its employees.
This site is intended for Australian residents only. Please review the Boston Scientific Privacy Policy, for practices on the collection, storage, use and disclosure of your personal information.
CAUTION : Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labelling supplied with each device.
References
- Ostrowski I. Slediz E. Ciechan J. et al. Current interventional management of male stress urinary incontinence following urological procedures. Cent European J Urol. 2015;68:340–347.
- Rehder P. Haab F. Cornu J-N. et al. Treatment of postprostatectomy male urinary incontinence with the transobturator retroluminal repositioning sling suspension: 3-year follow-up. Eur Urol. 2012;62(1):140–145.
- Viers BR, Linder BJ, Rivera ME, Rangel LJ, Ziegelmann MJ, Elliott DS. Long-Term Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes among Primary and Secondary Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantations in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence. J Urol. 2016; 196 (3): 838-43.
- Riemsma R, Hagen S, Kirschner-Hermanns R, Norton C, Wijk H, Andersson KE, Chapple C, Spinks J, Wagg A, Hutt E, Misso K, Deshpande S, Kleijnen J, Milsom I. Can incontinence be cured? A systematic review of cure rates. BMC Med. 2017; 15 (1): 63.
- Cordon BH. Singla N. Singla AK. Artificial urinary sphincters for male stress urinary incontinence: current perspectives. Med Devices (Auckl). 2016; 9:175–183.
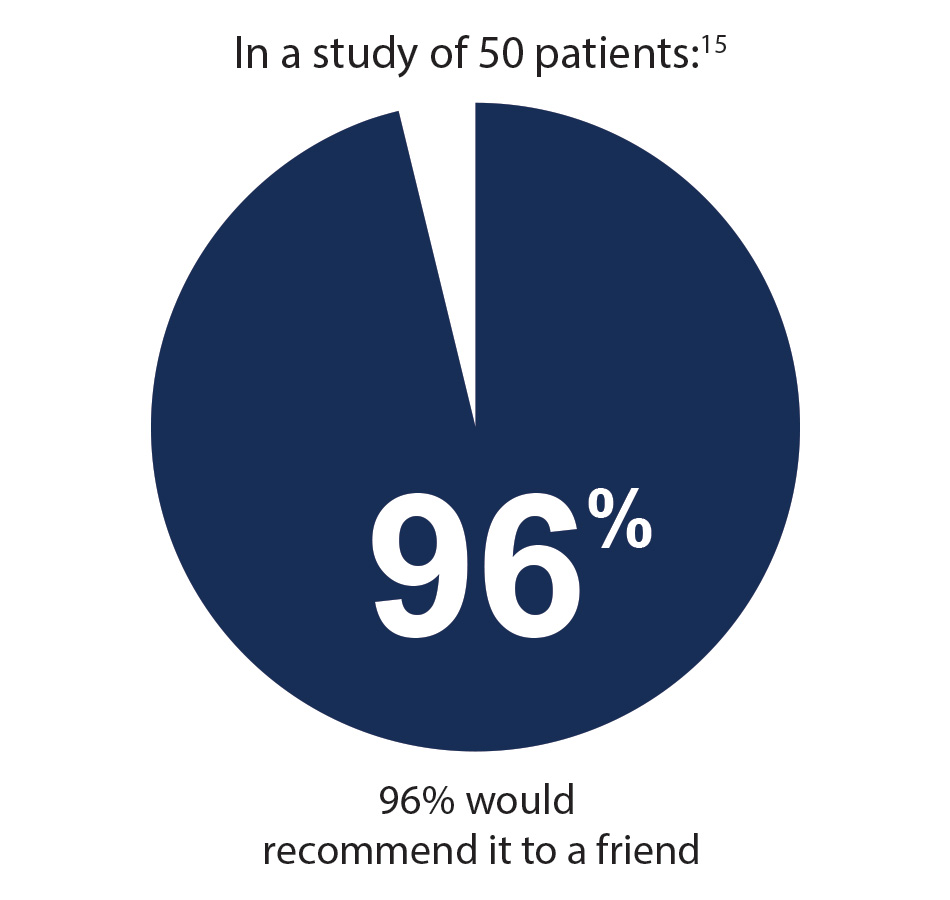
- Comiter CV. Dobberfuhl AD. The artificial urinary sphincter and male sling for postprostatectomy incontinence: which patient should get which procedure? Investig Clin Urol. 2016;57:3–13.
- Welk BK. Herschorn S. The male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a review of contemporary sling designs and outcomes. Br J Utol Int. 2011;109:328–344.
- AdVance™ Male Sling System Instructions for Use. American Medical Systems, Inc. 2010.
- Suskind AM. Bernstein B. Murphy-Setzko M. Patient-perceived outcomes of the AdVance sling up to 40 months post procedure. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(7):1267–1270.
- Bauer R. Mayer ME. May F. et al. Complications of the AdVance transobturator male sling in the treatment of male stress urinary incontinence. Urology 2010;75:1494–1498.
- DeRidder D, Webster G. Clinical overview of the AdVance male sling in post-prostatectomy incontinence. Eur Urol (Suppl). 2011;10:401–406.
- AMS 800™ Urinary Control System Operating Room Manual. American Medical Systems, Inc. 2011.
- AMS 800™ Urinary Control System Instructions for Use. American Medical Systems, Inc. 2011.
- Van der Aa F. Drake MJ. Kasyan GR. et al. The artificial urinary sphincter after a quarter of a century: a critical, systematic review of its use in male non-neurogenic incontinence. Eur Urol. 2013;63(4):681–689.
- AMS 800™ Urinary Control System Instructions for Use. American Medical Systems, Inc. 2017.
- Poole K, Kerlin M, Wynne R. Prevalence and characteristics of urinary incontinence in a cohort of patients with chronic heart failure. Heart Lung. 2017; 46 (2): 67-73. https://www.heartandlung.org/article/S0147-9563(16)30224-2/fulltext.
- Harris SS. Link CL. Tennstedt SL. et al. Care seeking and treatment for urinary incontinence in a diverse population. J Urol. 2007;177:680–684.
- Jarvis TR, Chughtai B, Kaplan SA. Testosterone and benign prostatic hyperplasia.Asian J Androl. 2015;17(2):212-6.